Incorporating Composting into Your Home Garden: A Beginner’s Guide to Sustainable Practices

Embrace Sustainability in Your Garden
Integrating sustainable practices into gardening can significantly benefit both the environment and your plants. With the rising awareness of our environmental footprint, it’s vital to adopt methods that not only enhance your garden but also contribute positively to the planet. Composting stands out as one of the most effective ways to achieve this dual goal. This guide will explore the fundamentals of composting, empowering you to create a greener and more sustainable garden.
Why Composting Matters
Composting is more than just a gardening trend; it’s a holistic approach that transforms organic waste into a powerful resource for plant nutrition. Understanding why composting is essential can inspire even the most novice gardener. Consider these benefits:
- Reduces landfill waste: An estimated 30% of what we throw away is organic material that could be composted. By diverting kitchen scraps, such as vegetable peels, coffee grounds, and eggshells, along with yard waste like leaves and grass clippings, we can significantly decrease landfill contributions.
- Improves soil health: Compost enriches soil by adding vital nutrients, enhancing moisture retention, and fostering an ideal environment for healthy root development. Healthy soil is the cornerstone of a thriving garden, and compost acts as a natural fertilizer free from chemicals.
- Supports biodiversity: Incorporating diverse materials into your compost pile encourages a vibrant microbial community. This biodiversity is essential for disease resistance in plants and creates a balanced ecosystem, which is vital for sustainable gardening.
Getting Started
Starting your composting journey can seem daunting, but it can be quite simple with the right approach. Here are a few straightforward steps to set you on the path to effective composting:
- Choose a compost bin: Select a compost bin that fits your space and lifestyle. Options range from tumblers that speed up the process to traditional compost piles or bins that allow for easy mixing and aeration. For those with limited space, several compact and aesthetically pleasing containers are designed for urban settings.
- Know what to compost: The materials you can compost are plentiful. Besides kitchen scraps and yard waste, you can add coffee filters, shredded paper, and even small amounts of hair or fur. Avoid adding meat, dairy, and oils, as these can attract unwanted pests.
- Maintain the compost: Regularly turning the compost pile is crucial for aeration, which facilitates faster decomposition. This action helps create the ideal environment for microorganisms to break down the organic material. Keeping the right balance of ‘greens’ (nitrogen-rich materials) and ‘browns’ (carbon-rich materials) is also vital for optimal results.
As you venture into the world of composting, you’ll uncover a wealth of knowledge and satisfaction from witnessing the transformation of waste into a wonderful resource for your garden. Allow the natural processes of decomposition to work in your favor, and get ready to cultivate a thriving, sustainable garden right from your backyard!
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to get started on your gardening journey!
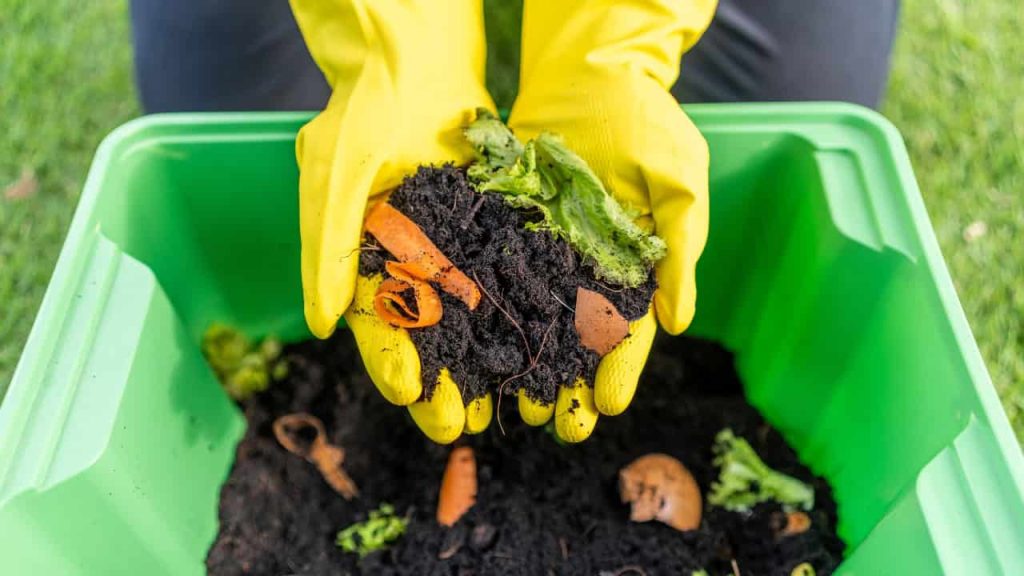

The Fundamentals of Composting
Before diving into the practical aspects of composting, it’s important to grasp the fundamental principles that underpin this eco-friendly practice. Composting mimics nature’s process of decomposition, transforming kitchen scraps and yard waste into nutrient-rich organic matter. This natural recycling process enriches your soil and reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, making it a cornerstone of sustainable gardening.
Understanding the Composting Process
The journey from kitchen waste to compost involves several stages. It begins with the collection of materials, both ‘greens’, which provide nitrogen, and ‘browns’, which supply carbon. The ideal ratio is roughly three parts browns to one part greens. This balance fosters an environment where microorganisms thrive, breaking down the organic matter efficiently. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the composting process:
- Microbial Action: Tiny microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi, are the unsung heroes of composting. They feed on the carbon and nitrogen-rich materials, breaking them down into simpler substances. This phase takes anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on various factors like moisture, temperature, and aeration.
- Heat Generation: As microorganisms consume the organic material, they produce heat. A well-maintained compost pile can reach temperatures of 130°F to 160°F, which aids in further decomposition and helps kill off pathogens and weed seeds, ensuring the safety of your compost.
- Humification: Following the microbial breakdown and heat generation comes the transformation into humus, the stable organic matter in compost that provides plants with essential nutrients. A fully decomposed compost will have a dark, crumbly texture and a pleasant earthy smell, indicating it’s ready to be used in your garden.
Tips for Successful Composting
<pTo reap the maximum benefits from your composting efforts, consider these essential tips:
- Maintain Moisture Levels: Compost piles should be kept moist, similar to a wrung-out sponge. Insufficient moisture can slow down the decomposition process, while excess moisture can lead to odor issues. Regularly check the dampness and adjust by adding dry materials or some water as necessary.
- Aerate Regularly: Turning your compost pile every few weeks introduces oxygen, which is essential for aerobic decomposition. This not only accelerates the composting process but also helps combat odors that may arise from anaerobic conditions.
- Monitor Temperature: Keeping an eye on the temperature of your compost can provide insights into its health. If the pile is too cold, consider adding more greens or turning it to introduce oxygen. Conversely, if it’s too hot, you might need to include more browns to balance the nitrogen content.
Composting is not just a simple act of tossing scraps into a bin; it’s an engaging process that allows you to connect with nature while promoting sustainable practices within your home garden. As you start to experiment with the ins and outs of composting, you’ll discover its incredible potential to transform your garden and contribute positively to the planet.
Understanding Composting and Its Benefits
Composting is a natural process that transforms kitchen scraps and yard waste into nutrient-rich soil amendments. By adopting composting practices in your home garden, you can significantly improve your soil health, reduce waste sent to landfills, and foster a more sustainable environment. Let’s delve deeper into the advantages of composting that every beginner should know.
| Category | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Nutrient-Rich Soil | Composting enriches the soil, providing essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. |
| Waste Reduction | Composting reduces the volume of organic waste sent to landfills, significantly lowering greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Enhanced Soil Structure | Improves aeration and water retention in the soil, promoting better plant growth. |
The process of composting creates a diverse ecosystem of beneficial microorganisms that break down organic matter. This transformation not only produces compost but also encourages biodiversity in your garden. The resulting compost can help suppress plant diseases and pests while enhancing the overall health of your plants.Furthermore, integrating composting into your gardening routine is a straightforward and rewarding practice. With just a small investment in compost bins or piles, you can create a system that supports a sustainable future while providing your garden with the nourishment it deserves. As you embark on this composting journey, remember that patience is key; the process may take time, but the benefits are profound.
EXPLORE MORE: Click here for expert tips on growing herbs indoors
Gathering Materials for Your Compost
To start composting effectively, understanding what materials to use is paramount. Home composting typically revolves around two primary categories of materials: ‘greens’ and ‘browns’. ‘Greens’ are high in nitrogen and include items like vegetable scraps, fruit peels, coffee grounds, and yard trimmings. On the other hand, ‘browns’ provide essential carbon and can consist of dried leaves, straw, cardboard, and small branches. Here’s how to gather and prepare your compost materials:
- Kitchen Scraps: A large portion of your compost can come from the kitchen. Keep a bin next to your sink to conveniently collect vegetable peelings, eggshells, and even stale bread.
- Yard Waste: During lawn maintenance, collect grass clippings, plant trimmings, and fallen leaves. These materials not only bulk up your compost but also help to maintain essential aeration within the pile.
- Paper and Cardboard: Non-glossy paper and cardboard can be shredded and added to the compost. However, it’s crucial to avoid materials with shiny finishes or heavy ink as they may not decompose effectively and could introduce toxins.
- Avoid Certain Items: As you gather materials, steer clear of meat, dairy, oily foods, and pet waste, as these can attract pests and create odor problems.
Choosing the Right Composting System
Your choice of a composting system significantly impacts the ease and efficiency of your composting journey. Various methods cater to different space constraints and preferences. Here are some options to consider:
- Traditional Compost Piles: If you have ample space, a traditional compost pile can be the most straightforward method. Simply stack your materials in a designated area, turning them regularly for aeration.
- Compost Bins: For a more contained approach, compost bins are available in various sizes and materials. They can help contain odors while providing excellent airflow, making them ideal for home gardens.
- Worm Composting (Vermicomposting): If your space is limited, consider vermicomposting, which involves using worms to break down organic matter. This method produces nutrient-rich worm castings, a highly sought-after compost variant.
- Bokashi Composting: Popular in many cultures, bokashi composting uses a fermentation process. Kitchen waste is layered with bokashi bran (rich in beneficial microbes) and kept airtight until it’s added to soil or a traditional compost system.
Utilizing Your Compost for Garden Success
Once your compost is ready, it’s time to put it to use in your garden. Applying compost enriches the soil, enhancing its structure, fertility, and water retention capacity. Here are some practical ways to utilize your finished compost:
- Soil Amendment: Mix your compost with existing soil when preparing garden beds. This ensures that essential nutrients are readily available for your plants.
- Mulching: Spread a layer of compost on the surface around your plants to suppress weeds and retain moisture while gradually enriching the soil as it breaks down further.
- Potting Mix: Create your custom potting mix by blending equal parts compost, peat moss, and perlite or coarse sand. This makes for a light and nutrient-rich medium for container plants.
As you embark on your composting adventure, embrace the learning curve. Each batch will teach you more about the delicate balance of materials and the process itself. By incorporating composting into your home garden, you’re not only fostering a healthier environment for your plants but also aligning with sustainable practices that benefit the planet.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to learn how to choose harmonious vegetable companions
Conclusion: Embracing Composting for a Sustainable Future
Incorporating composting into your home garden represents a remarkable step towards sustainable living, one that can yield substantial benefits not only for your plants but for the environment as a whole. By understanding the essential balance of ‘greens’ and ‘browns’, and exploring various composting methods, you can transform kitchen scraps and yard waste into black gold that enriches your soil.
As you journey into the world of composting, it’s important to remember that this process is not only about recycling waste but also about nurturing a vibrant ecosystem in your garden. Composting can enhance the health of your plants, improve soil structure, and reduce your carbon footprint—all while minimizing waste sent to landfills.
Moreover, each compost batch you create will deepen your understanding of organic gardening practices and contribute to biodiversity. As you experiment with various techniques—whether it be traditional piles, bins, or vermicomposting—don’t hesitate to share your experiences with friends and neighbors. Building a community around sustainable gardening can amplify the positive impact of your efforts.
So, as you step into the garden with your rich, homemade compost, remember you are cultivating more than just plants. You are fostering a lifestyle that values environmental stewardship and sustainability. For those eager to dive deeper, consider local workshops or online resources that focus on advanced composting techniques or sustainability in gardening. The journey is just beginning, and every small effort counts!