Seasonal Planting: How to Choose Native Crops for Sustainable Home Gardening

Explore the Benefits of Seasonal Planting
Growing your own food not only brings joy but also fosters a deep connection with nature. One of the most effective ways to ensure a thriving home garden is by focusing on seasonal planting. By selecting crops that are native to your region, you can enhance biodiversity while promoting sustainability. This approach is particularly salient in the United States, where climatic diversity allows for a wide range of crops tailored to local conditions.
Why Choose Native Crops?
Native crops offer a wealth of advantages for home gardeners. Here are a few compelling reasons to consider:
- Adaptation: Native plants are well-suited to local climate and soil conditions, making them easier to grow. For example, the Butterfly Bush in the Midwest and the California Poppy on the West Coast thrive in their respective environments, ensuring a higher success rate for gardeners.
- Resilience: They naturally resist pests and diseases, thereby reducing the need for chemical interventions. Crops like American Hazelnut or Wild Rice exhibit a natural robustness against common pests, making them a safer choice for both your garden and the ecosystem.
- Support Biodiversity: Planting natives encourages local wildlife, including pollinators, to thrive in your garden. Bees, butterflies, and even birds benefit from native flora, which in turn supports pollination and increases the productivity of your home garden.
As seasons change, so do the opportunities to grow these native plants. Incorporating them into your gardening routine not only maximizes yields but also minimizes environmental impact. Seasonal planting allows for a dynamic gardening experience, adapting to the rhythms of nature.
Getting Started with Seasonal Planting
To begin your journey into sustainable home gardening, consider these actionable steps:
- Research Native Species: Identify which crops are best suited for your area throughout the year. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map can be a helpful resource in determining what will thrive in your region. For instance, if you reside in Zone 5, you might find success with peas in spring and pumpkins in the fall.
- Plan Your Garden: Design your garden layout with the seasonal changes in mind. A well-planned garden integrates crop rotation, intercropping, and seasonal shifts to maximize space utilization and yield. For example, after harvesting quick-growing leafy greens, you can plant a hardy root vegetable for the next season.
- Simple Guidelines: Follow seasonal planting guidelines to ensure healthy growth and harvest. Local agricultural extensions offer valuable crop calendars that outline planting windows for various species in your state. These resources assist in timing your planting to avoid unexpected frosts or droughts.
By embracing seasonal planting and native crops, you’ll contribute not only to your household’s sustainability but also to the broader ecological health of your community. Each choice you make in your garden can resonate beyond your backyard. Explore the incredible variety of native crops available to you today and cultivate a garden that not only feeds you but also enriches your local environment!

DIVE DEEPER: Click here for a complete guide
Choosing the Right Native Crops for Your Garden
To make the most out of your seasonal planting endeavors, it’s crucial to select native crops that not only fit within your local environment but also align with the seasons. Understanding your region’s climate, soil types, and the ecological needs of native plants can dramatically affect your gardening success. Most importantly, it allows you to contribute positively to local ecosystems by using crops that have co-evolved with the environment.
Understanding Your Local Climate
The climate varies significantly across the United States, from humid subtropical zones in the Southeast to arid regions in the Southwest. Recognizing your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone can be a vital first step in selecting crops that will thrive. For example:
- In warmer zones like Zone 10 (Southern California), you may consider planting avocados and citrus fruits, which flourish in rich, well-drained soils with abundant sunlight.
- Conversely, in cooler regions such as Zone 3 (Northern Minnesota), crops like kale and carrots are more suitable, capable of withstanding the chill of early spring and late fall.
Consult local gardening guides or cooperative extension services to gather specific information about growth habits, soil preferences, and optimal planting times for various crops. This knowledge not only empowers you as a gardener but also helps you choose the right native species to improve your garden’s sustainability.
Seasonal Planting Techniques
With an understanding of your local climate, the next step involves honing in on seasonal planting techniques. Embracing a strategy that aligns with the seasons can lead to increased productivity and reduced resource consumption. Here are several methods worth considering:
- Succession Planting: This technique involves planting a new crop immediately after harvesting an existing crop. For instance, after a successful harvest of lettuce in the spring, you might follow up with a summer planting of green beans.
- Intercropping: This method entails planting multiple crops in proximity for mutual benefit. For example, pairing corn with beans and squash (the traditional “Three Sisters” planting) not only maximizes space but also enhances soil health as the crops support each other’s growth.
- Companion Planting: Certain plants naturally deter pests or enhance each other’s growth. For instance, planting marigolds alongside your vegetables can protect them from harmful pests and promote a healthier garden environment.
Exploring these techniques within the context of seasonal planting can significantly boost your home garden’s productivity while minimizing your ecological footprint. By strategically choosing native crops that align with your garden’s seasonal changes, you pave the way for a sustainable and rewarding gardening experience.
Understanding the Importance of Native Plants in Sustainable Gardening
When considering sustainable home gardening, the choice of crops can significantly impact both your garden’s health and the local ecosystem. Native plants, specifically, are adapted to your region’s climate, soil, and pests, making them a fantastic option for minimizing water usage, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers, and requiring less maintenance overall. They also provide vital habitats for local wildlife, including pollinators like bees and butterflies, which are essential for successful fruit and vegetable production.Furthermore, native crops are often more resilient to the challenges posed by local climatic conditions, such as droughts or heavy rains. By selecting crops that have evolved in a particular area, gardeners can enjoy the beauty and productivity of their gardens while contributing to biodiversity conservation. For instance, incorporating varieties of native fruits and vegetables not only enhances culinary diversity but also enriches the soil, supporting the broader ecosystem around your home.In addition to ecological benefits, growing native plants can yield significant economic advantages. Home gardeners can reduce costs related to watering and pest control, as native species typically require less intervention. This sustainable approach ultimately fosters a more self-sufficient gardening practice, allowing you to produce fresh, organic food right at your doorstep.
Tips for Selecting Native Crops
To embark on your journey of seasonal planting with native crops, it’s vital to consider several factors. Start by researching plants that are native to your specific area; local extension services or botanical gardens can provide invaluable resources. Pay attention to the specific seasons when these native crops thrive, ensuring you plant them at the optimal time for growth.Additionally, design your garden layout by grouping plants with similar sunlight and water requirements. This strategy not only maximizes your garden’s productivity but also mirrors natural ecosystems, contributing positively to their health and longevity. As you cultivate your native garden, keep an eye out for companion planting opportunities, as certain combinations can promote growth and reduce pest populations.By meticulously selecting and cultivating native plants, you’re not just enhancing your garden; you’re promoting a sustainable future, making a difference one crop at a time. For those keen on exploring this rewarding venture further, consider consulting local gardening clubs or online platforms dedicated to sustainable gardening practices. The possibilities for creating a lush, thriving garden filled with native crops are endless, with benefits that extend far beyond the backyard.
DIVE DEEPER: Click here to learn how to start your compost bin
Enhancing Biodiversity through Native Choices
Embracing native crops in your seasonal planting not only garners a thriving garden but also contributes to enhancing local biodiversity. Native plants play a pivotal role in supporting the ecosystem, attracting crucial pollinators, and creating habitats for wildlife. By selecting the appropriate native crops, you can create a balanced garden that echoes the natural landscape of your area.
The Role of Native Plants in Biodiversity
Native plants are the backbone of local ecosystems. They have evolved over time to adapt to specific climates, insects, and soil types, making them well-suited to grow with minimal inputs. This innate resilience can positively impact your home garden by:
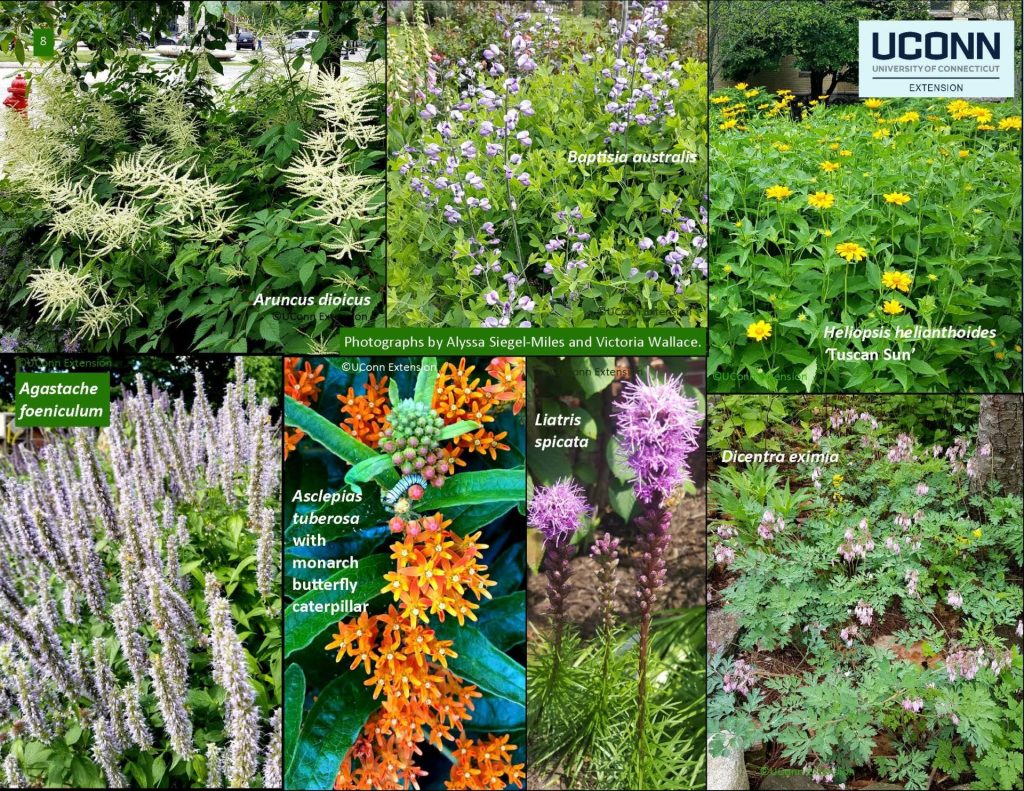
- Attracting Pollinators: By incorporating native flowering crops such as purple coneflower or butterfly weed, you can attract essential pollinators like bees and butterflies. These beneficial insects enhance fruit and vegetable production, leading to a more bountiful harvest.
- Providing Food and Shelter: Native fruit-bearing plants like blackberries or plums serve as nourishment for local wildlife, while shrubs such as serviceberry create nesting sites for birds. This interconnected system leads to a thriving ecosystem right in your backyard.
- Encouraging Soil Health: Native crops are often deep-rooted, enhancing soil aeration and reducing runoff. Their natural growth can lead to improved soil structure and fertility, ensuring a robust environment for other plants to thrive.
Utilizing Local Expertise for Crop Selection
While the internet provides a wealth of information, tapping into local resources can give you a more nuanced understanding of your gardening choices. Engaging with local gardening clubs or native plant societies can broaden your knowledge base. These groups usually have a wealth of information on:
- Specific Native Varieties: These organizations can help identify crops native to your region. For example, the Native Plant Society in your state may host forums that connect you with seasoned gardeners who can share their firsthand experiences.
- Planting Workshops: Many communities host workshops to educate gardeners on native plants and sustainable practices. Participating in these workshops enables you to gain hands-on experience, fostering both practical skills and local connections.
- Seasonal Planting Calendars: Understanding the best planting and harvesting timings for each native crop can be vital. Many local extension services provide calendars that inform you about the best months to sow, transplant, and harvest various crops.
By incorporating local expertise and knowledge, you’ll be able to develop a more robust and resilient garden that aligns with your community’s ecological needs and seasonal variations.
Thinking Beyond Aesthetic Appeal
While colorful native blooms and lush foliage can undoubtedly enhance the aesthetic of your garden, it’s essential to consider the ecological impacts of your plant choices. Native crops often require less irrigation, which is vital in regions prone to drought. Furthermore, incorporating permaculture principles can lead to a garden that is self-sustaining and resilient. Strategies such as planting groundcovers like clover can naturally enrich the soil, reduce weed growth, and conserve moisture.
Overall, making informed choices about native crops allows you to not only cultivate a garden that reflects the beauty of your local landscape but also contributes to the broader ecological tapestry, fostering a sense of responsibility toward the environment. As you embark on your journey into seasonal planting, keep these principles and insights in mind to ensure that your garden thrives while supporting the ecosystem that surrounds it.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to learn about rainwater harvesting
Conclusion: Embracing Native Crops for Sustainable Growth
In the journey of seasonal planting, embracing native crops offers a transformative approach to home gardening that goes beyond mere aesthetics. By opting for plants that are native to your region, you contribute to ecological balance, enhance biodiversity, and foster a sustainable environment. The benefits of incorporating native varieties—such as attracting vital pollinators, providing food and shelter for wildlife, and promoting soil health—create a thriving ecosystem right in your backyard.
Moreover, leveraging local resources, expertise, and community knowledge enables you to make informed decisions on which crops will flourish best in your specific area. Engaging in planting workshops, consulting local botanical societies, and understanding seasonal calendars ensures that you are well-prepared to cultivate a garden that aligns with both personal and ecological goals. This collective effort not only supports local wildlife but also nurtures a sense of stewardship and connection to the land.
As you embark on your sustainable gardening journey, remember that the choices you make today will have lasting impacts for generations. Infusing your garden with native crops promotes resilience and sustainability, all while providing a space that brings you joy and nourishes both body and spirit. Investigate, learn, and ultimately create a garden that reflects your commitment to the environment and recognizes the beauty of your local landscape. In the world of home gardening, your efforts can pave the way for a greener future.