Sustainable Irrigation Techniques: Organic Methods for Efficient Plant Hydration

Understanding Water Scarcity in Agriculture
The link between water scarcity and agriculture has become increasingly evident, especially as farmers face prolonged droughts and unpredictable rainfall caused by climate change. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, agriculture accounts for approximately 80% of the nation’s freshwater usage. This statistic highlights the urgency of adopting methods that maximize water efficiency without compromising crop health.
The Role of Sustainable Irrigation Techniques
In the face of such challenges, employing sustainable irrigation techniques has risen to the forefront of agricultural practices. These techniques not only conserve water but also enhance the overall quality of the soil, which is vital for productive farming. Here are several innovative methods that farmers across the United States are increasingly adopting:
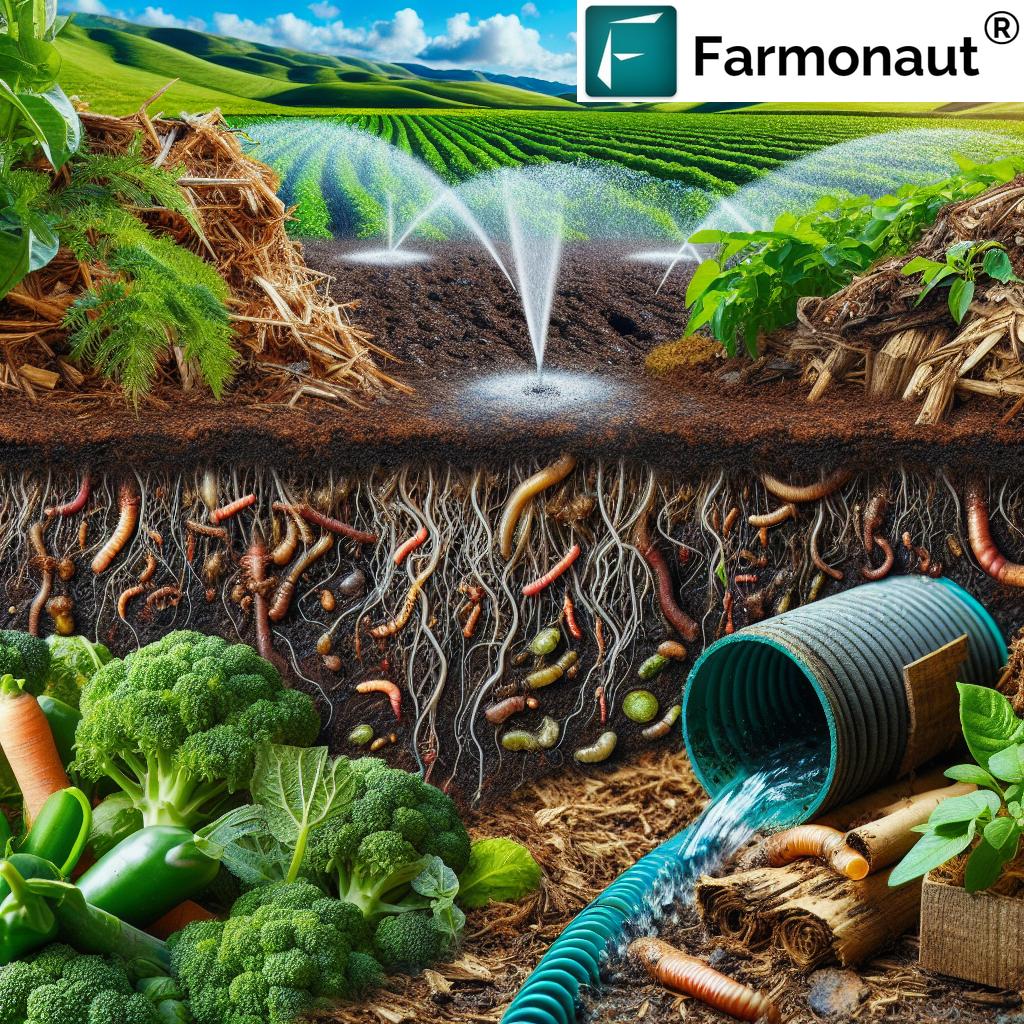
- Drip Irrigation: This precise watering technique employs a network of tubing and emitters to deliver water directly to the root zone of the plants. It drastically reduces evaporation and runoff, which are common challenges with traditional irrigation methods. For instance, farms in California’s Central Valley have reported up to a 60% reduction in water usage by switching to drip systems.
- Rainwater Harvesting: By capturing rainwater through gutters and storage systems, farmers can significantly decrease their reliance on conventional water sources. An illustrative example can be seen in Hawaii, where farmers utilize this method not only for irrigation but also for maintaining crop resilience during dry spells.
- Mulching: This organic technique involves covering the soil with materials such as straw or wood chips, which helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. It is particularly effective in arid regions where soil moisture conservation is critical for crop sustainability.
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Investing in technology, such as soil moisture sensors, allows farmers to monitor soil hydration levels closely. By applying water only when necessary, farmers can avoid over-irrigation—saving both water and costs. This precision farming approach has gained traction in states like Texas where extensive agriculture spans vast areas.
The Importance of Adopting Organic Methods
These organic irrigation techniques extend beyond mere water savings; they contribute to the long-term vitality of agricultural practices. Soil health is vital for crop productivity and by utilizing methods like mulching and rainwater harvesting, farmers invest in a sustainable future.
As we explore each technique further, it becomes evident how sustainable irrigation is not just a trend but a necessary evolution in farming practices. By implementing these solutions, farmers can combat the looming threat of water shortages while promoting biodiversity and minimizing environmental impact. Through education and technological advancements, the agricultural sector can pave the way toward a more sustainable and resilient future.
Ultimately, the transition to sustainable irrigation not only addresses immediate needs but sets the groundwork for generations of farmers to come, ensuring that we protect our water resources while cultivating healthy crops that feed our communities.

DISCOVER MORE: Click here to delve into vertical gardening
Exploring Innovative Sustainable Irrigation Techniques
Sustainable irrigation is not merely a buzzword; it embodies a transformative shift in agricultural practices aimed at preserving vital water resources while promoting healthier ecosystems. As droughts become more frequent and water scarcity looms, farmers are increasingly turning to organic methods that allow them to optimize water use while maintaining the integrity of the soil and crops. Each of these techniques presents unique benefits and can lead to significant water savings, ultimately making farming more resilient in the face of climate change.
Drip Irrigation: The Precision Water Saver
Drip irrigation has emerged as one of the most effective sustainable irrigation practices. By delivering water directly to the plant roots through a network of tubes and emitters, this technique minimizes water loss through evaporation and runoff. Research shows that farms utilizing drip systems in states like California have achieved up to a 60% reduction in water usage, illustrating that efficiency can go hand-in-hand with crop health. This approach not only conserves water but enhances nutrient delivery, supporting healthier plants without the risk of over-saturation.
Rainwater Harvesting: Harnessing Nature’s Gift
Implementing rainwater harvesting allows farmers to capitalize on precipitation, capturing and storing rainwater for irrigation use. This practice not only reduces dependency on municipal water systems but also provides a buffer during dry spells. In various regions across the U.S., such as parts of Florida and Texas, farmers have installed rainwater collection systems to irrigate crops, effectively transforming what would be waste into a sustainable resource. Educational programs on this technique have sprouted, encouraging farmers to utilize this natural source effectively.
Mulching: An Organic Shield for Soil
Another prominent method, mulching, involves covering the soil with organic materials—such as straw, leaves, or wood chips—to retain moisture. This method is invaluable for water conservation, particularly in arid climates where evaporation rates are high. By regulating soil temperature and suppressing weed growth, mulching fosters a sustainable microclimate conducive to plant health. Many vegetable and fruit farms in states like Arizona and New Mexico have successfully integrated mulching into their farming systems, leading to improved yield and lower irrigation needs.
Soil Moisture Sensors: Technology Meets Tradition
In an age of rapid technological advancement, the integration of soil moisture sensors into farming practices has revolutionized irrigation management. These devices provide real-time data on soil hydration levels, enabling farmers to apply water only when absolutely necessary. This precision farming approach has shown substantial promise in regions, such as the Midwest, where extensive row cropping occurs. By reducing over-irrigation, farmers not only conserve water but also reduce energy costs associated with pumping and using water resources.
As the agriculture sector adapts to changing climates and the pressing challenge of water scarcity, the adoption of these sustainable irrigation techniques is vital. Such practices ensure that farmers can maintain productivity while safeguarding the environment against further degradation. By incorporating these innovative methods, farmers can contribute to a sustainable future that balances human needs with ecological integrity.
Sustainable Irrigation Techniques: Organic Methods for Efficient Plant Hydration
As we explore sustainable irrigation techniques, it becomes vital to consider various organic methods that not only enhance plant hydration efficiency but also contribute positively to environmental sustainability. Utilizing organic practices can ensure that the resources are used judiciously, minimizing waste and preventing soil degradation.
One popular method in organic irrigation is the implementation of drip irrigation systems. This technique delivers water directly to the roots of the plants, thereby reducing evaporation and runoff. Moreover, it ensures that plants receive water at a consistent rate, which is crucial for their growth and overall health. With drip irrigation, farmers can save up to 50% of their water usage compared to traditional methods.
Another innovative approach is the use of rainwater harvesting. By collecting and storing rainwater, growers can significantly reduce their reliance on groundwater resources. This method not only conserves water but also protects plants from over- or under-watering, promoting healthier growth. Additionally, integrating rainwater systems with gardens or farms can bolster local ecosystems and enhance biodiversity.
Implementing mulching techniques is another organic method that helps retain soil moisture, reduce soil temperature, and suppress weed growth. Organic materials such as straw, grass clippings, or wood chips can be used as mulch, enriching the soil as they decompose and providing a feed for beneficial microbes. This creates a sustainable cycle of hydration and nourishment for the plants.
Lastly, permaculture design offers a holistic approach to sustainable irrigation. This method encourages the cultivation of ecosystems that naturally maintain soil health and moisture. By designing landscapes that mimic natural processes, permaculture reduces the dependency on artificial irrigation systems and guides water naturally to where it is needed.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | Direct water delivery to roots, minimizing evaporation. |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Collecting rain for irrigation, reducing groundwater reliance. |
| Mulching Techniques | Using organic materials to retain moisture and enrich soil. |
| Permaculture Design | Creating natural ecosystems that maintain moisture organically. |
By employing these organic methods, we can pave the way for a more sustainable approach to plant hydration, ensuring both current and future generations have access to essential water resources. The exploration of such techniques not only reveals their practicality but also elicits a deeper understanding of nature’s intricate balance. As the momentum for sustainability grows, so does the imperative to delve further into these innovative practices.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to learn how to start your own organic garden!
Maximizing Efficiency Through Advanced Organic Practices
The global agriculture community has an invaluable opportunity to explore organic irrigation techniques that not only address water scarcity but also enhance soil health and crop resilience. As the pressure mounts from environmental challenges, innovative methods are leading the charge toward sustainable farming, especially in regions prone to drought and fluctuating rainfall patterns. Among the transformative practices gaining traction, permaculture techniques and subsurface irrigation have emerged as remarkable alternatives, each offering sustainable solutions tailored to specific agricultural needs.
Permaculture: A Design for Resilience
Permaculture, a design approach that focuses on creating sustainable and self-sufficient agricultural systems, integrates various techniques, including organic irrigation methods, to optimize water resources. By mimicking natural ecosystems, permaculture encourages farmers to design their landscapes to capture and retain water effectively. Swales—shallow trenches along the contour of the land—are one example; they help direct water flow and enhance infiltration, reducing runoff and soil erosion.
This method not only fosters efficient water use but also builds soil fertility. By incorporating cover crops and intercropping techniques, farmers can improve the organic matter in the soil. In states like California, where water conservation is paramount, permaculture has shown promise in creating resilient farming systems that yield productive results while minimizing resource consumption.
Subsurface Irrigation: Below the Surface Efficiency
Subsurface irrigation involves burying drip tubes or porous pipes beneath the soil surface, allowing water to percolate directly to the roots of plants. This method significantly reduces evaporation and runoff, making it a fantastic solution for crops in drier regions. With its increased efficiency, subsurface irrigation has been implemented widely in areas across Texas and New Mexico, yielding promising results for crops like cotton and vegetables.
Recent studies highlight that farms implementing subsurface systems can achieve water savings of up to 50% compared to more traditional methods. Additionally, by minimizing water exposure to the air, subsurface irrigation helps maintain soil structure and temperature, fostering a healthier root environment and promoting nutrient uptake.
Crop Rotation: A Vital Component
Crop rotation is another sustainable practice that supports efficient water management. By alternating crops in succession, farmers enhance soil structure, reduce disease prevalence, and minimize pest pressures. This method improves the soil’s ability to retain moisture and enables more efficient irrigation practices.
For farmers focused on organic methods, crop rotation is a natural fit, as it allows for greater biodiversity and reduces reliance on chemical inputs. This age-old technique remains relevant today, especially in regions like the Midwest, where varying types of crops, such as soybeans and corn, are rotated to optimize water usage and improve resilience against drought conditions.
Wetlands and Biodiversity: Natural Water Filters
Integrating wetlands into agricultural landscapes can also enhance sustainable irrigation practices. These natural features serve as both water filters and reservoirs, helping to regulate water flow and mitigate flooding. Farmers near wetland areas have reported increased crop yields and reduced irrigation demands, thanks to natural biodiversity contributing to soil health. Moreover, wetland restoration projects can foster ecosystem stability and positively impact local wildlife habitats.
As farmers adopt and experiment with these sustainable irrigation techniques, the interconnectedness between responsible water use, healthy soil, and productive ecosystems becomes increasingly apparent. Embracing these organic methods not only leads to effective plant hydration but also lays the groundwork for a resilient agricultural future. Harnessing innovative practices today ensures that future generations can thrive in harmony with the environment, creating lasting sustainability for our vital water resources.
DIVE DEEPER: Click here to learn how to identify and treat indoor plant pests</
Looking Ahead: A Sustainable Future in Irrigation
In conclusion, the adoption of sustainable irrigation techniques is essential for addressing the growing challenges of water scarcity and environmental degradation. The innovative practices highlighted, such as permaculture, subsurface irrigation, and crop rotation, reflect a shift toward a more holistic approach to agriculture that emphasizes efficiency and resilience. These methods not only improve water management but also enhance soil health, contribute to biodiversity, and promote ecological balance.
As we face unprecedented climate fluctuations, embracing these organic methods provides a beacon of hope for farmers across the United States and beyond. For instance, by integrating wetlands into farming systems, not only are crops benefitting from natural filtration and water retention, but ecosystems are being preserved, showcasing the dual benefits of these practices. Furthermore, new research continually unveils the potential for even greater water savings and crop yields through advanced technologies paired with organic techniques.
Farmers, policymakers, and consumers alike play a pivotal role in cultivating sustainable practices that strengthen the link between agriculture and the environment. By prioritizing efficient plant hydration strategies and advocating for organic methods, we can ensure that our farming systems remain productive while safeguarding our precious water resources for generations to come. As the agricultural landscape evolves, it is imperative that we stay informed and proactive about the sustainable choices we make today for a resilient tomorrow.